Standardisation Process
EEBUS is the central process driver for generating the best solution with inputs from three areas: our working groups (WG’s), funded projects as well as standardisation and regulatory bodies. Process starting point are market ideas and requirements coming from our member companies or funded projects in which EEBUS interacts with other organisations. These market requirements are translated into use case specifications ready for standardisation.
The EEBUS specification experts team ensures consistency and interoperability among the various use cases and organises cross-industry ‘’Plugfests’’ for system verification of new use cases to be released. Our standardisation experts then transfer the use cases into the relevant standardisation bodies and committees. Being an open standard, released use cases are publicly available on our homepage to be download.
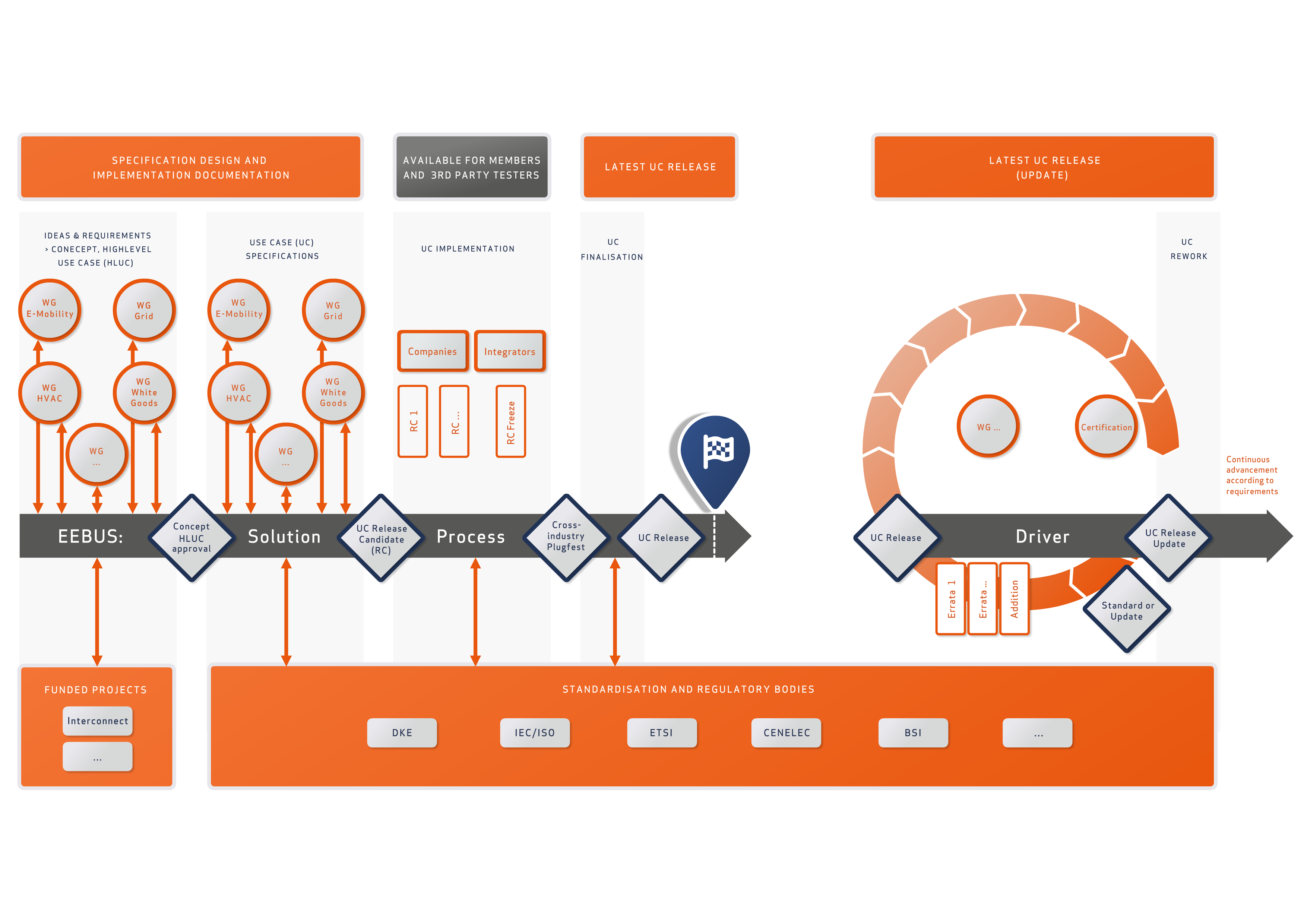
Release of the UC by:
- Review incl. risk analysis (e.g. FMEA)
- Plugfest
- Field testing of individual manufacturers
- Standardisation bodies
Translating market requirements into new standards
WORKING GROUPS
The working groups are an essential part of our EEBUS organisation: participating member companies actively shape the design of new use cases according to their market requirements. Experts from the companies meet with EEBUS specification engineers on a regular basis to jointly work out the use case specifications and enhance the underlying data model where required. Meeting agendas and minutes as well as the latest use case versions are available on a SharePoint where members can access.
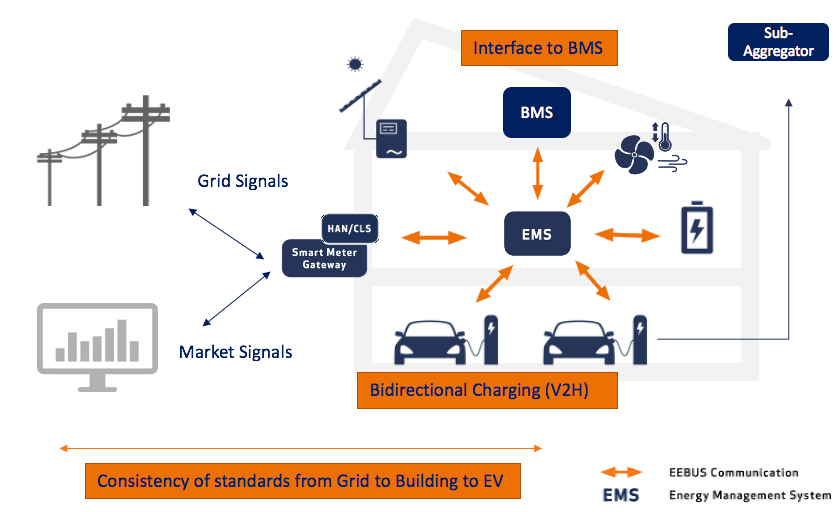
The philosophy of EEBUS is that all energy relevant devices from cross sector domains need to be able to interact and the interaction with the low-voltage grid needs to be properly managed. This cross-domain useability is well reflected in our working group structure. The following groups are working on the standard-based integration of domains into a broader and holistic eco system:
Overview of current EEBUS working groups
E-Mobility
Charging stations and electric vehicles
HVAC
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems

INVERTER
Photovoltaic and battery storage systems
GRID
Demand transparency and
set points by DSO
Standardisation
Standardisation
and legal framework
WORK Results
EEBUS
Solutions
Use Cases
are available for:
Power Limitation
Enables Distribution System Operators (DSO) to monitor power consumption on building or device level and to limit power consumption via temporary power limitations.
Dynamic Pricing
Preventive Capacity Allocation
Enables the DSO or ESP to adjust power curve of buildings or devices beforehand to avoid possible grid congestion or to participate in flexibility and balancing markets.
Self-Consumption Optimisation
Enables customers to benefit from local PV production over the day and to use stationary battery system or bi-directional EV-charging after sun set.
Additional Use Cases for Monitoring & Control (EMS)
Enables an increased flow of information for the EMS to optimise its operation and comfort functions for the customer.
All use cases may be used free of charge. A short high-level description of the EEBUS use cases, the phase model and the specification process can be found in the download area.
EEBUS
Use cases
Use case specifications
are available for:
E-Mobility
Grid Connection Point
Inverter
HVAC
EEBUS
technical backbone
The transmission of EEBUS SPINE data requires a transport protocol: EEBUS members have deliberately chosen an IP approach and developed the Smart Home IP (SHIP) transport protocol to be best-in-class with respect to cyber security and energy networking inside buildings.
Specifications
are available for:
Ship
Spine
EEBUS De Jure Standards
Today’s accelerating energy transition demands eco-systems to reach a critical mass. These eco-systems consists of a complex compilation of multiple energy relevant and controllable devices from numerous buildings. For the applied communication interface a de facto standard is not sufficient to ensure the necessary investment security. EEBUS therefore focuses on creating a de jure standard that allows for a secure investment in the development of mass market suitable serial products. EEBUS contributes with the experience and results from joint development of standards in important standardisation bodies and plays a key role in shaping future standards. Further domains for standardisation are being consistently promoted.
EEBUS
USE CASES
are standardised in
Local Charging station management systems and Local Energy Management Systems network connectivity and information exchange
IEC 63380-1
(in progress)
Household appliances network and grid connectivity
CENELEC EN 50631
Smart Appliances Reference Ontology Framework and M2M Mapping
EU Framework SAREF
ETSI TS 103 264
Technical exchange of information at the interface between the Grid Connection Point and the elements of the customer systems
VDE-AR-E 2829-6-1
VDE-AR-E 2122-1000
EEBUS
SPINE
Is standardised in
Local Charging station management systems and Local Energy Management Systems network connectivity and information exchange
IEC 63380-2, IEC 63380-3
(in progress)
Household appliances network and grid connectivity
CENELEC EN 50631
Smart Appliances Reference Ontology Framework and M2M Mapping
EU Framework SAREF
ETSI TS 103 264
Technical exchange of information at the interface between the Grid Connection Point and the elements of the customer systems
VDE-AR-E 2829-6-2
VDE-AR-E 2829-6-3
Standard interface for charging points/charging stations for connection to local power and energy management
VDE-AR-E 2122-1000
EEBUS
SHIP
is standardised in
Local Charging station management systems and Local Energy Management Systems network connectivity and information exchange
IEC 63380-3
(in progress)
Household appliances network and grid connectivity
CENELEC EN 50631
Technical exchange of information at the interface between the Grid Connection Point and the elements of the customer systems
„Standardisation is less about what is right and what is wrong but about balancing all interests and domains involved.“
EEBUS is active in the following important standardisation bodies:




EEBUS COOPERATIONS
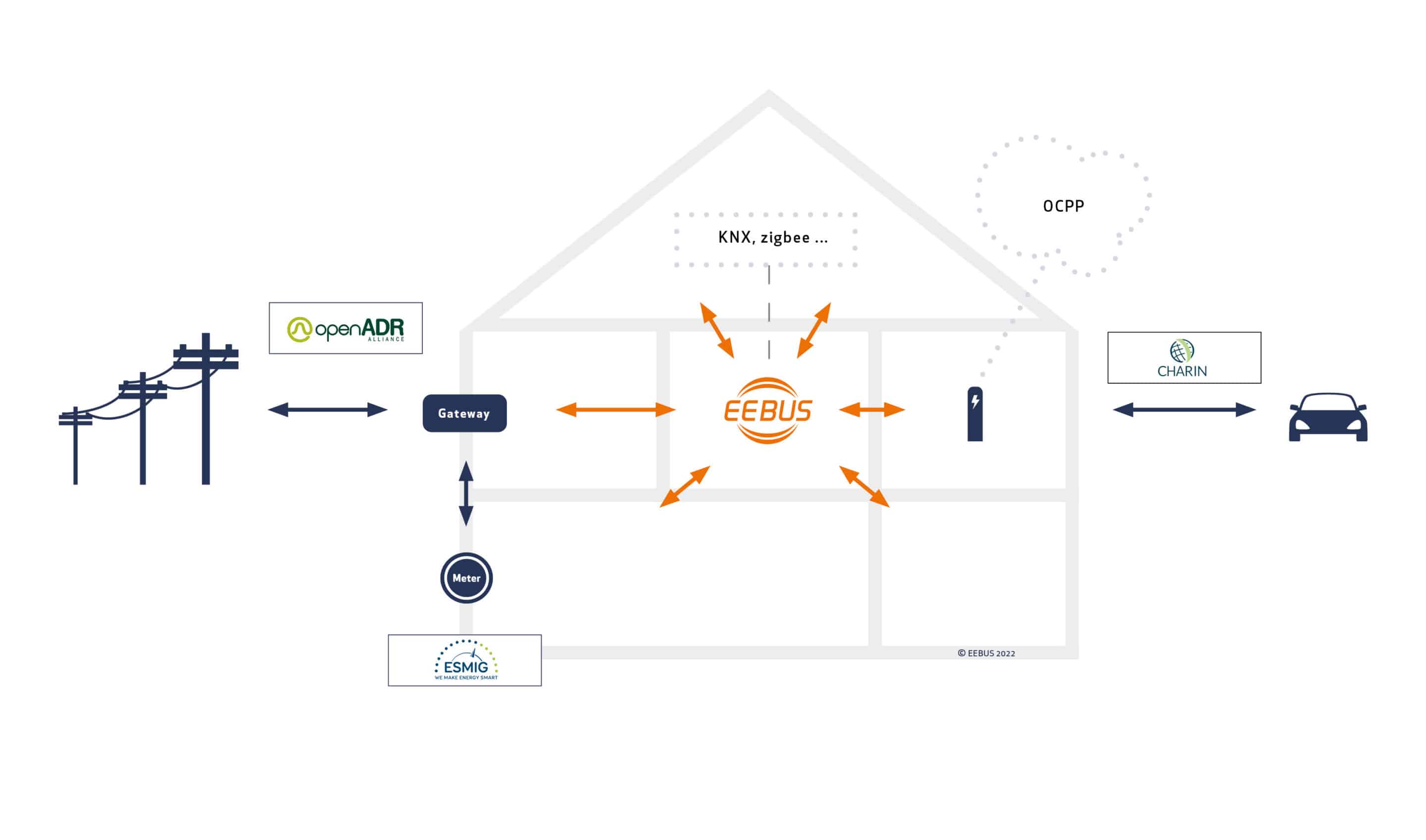
EEBUS is partnering with leading alliances and consortiums in Europe and the US: the common goal is to push forward the international harmonisation of the energy landscape for interoperable solutions. The integration of EEBUS, therefore, stands for reduced development costs and investment security for manufacturers.
Our partners:

OpenADR
For a standardised interface solution from smart grid to grid connection point

ESMIG
For a standardised interface solution from smart grid to smart meter

CharIn
For a standardised interface solution from grid connection point to electrical vehicle supply equipment
Cross Industry Network –
more than just a technical standard
The cross-industry network plays a central role in the energy transition and thus within EEBUS. Through the constant exchange of individual information, a common understanding is developed, creating the basis for new use cases and business models. Solutions around capacity and tariff management involve multiple players and a wide variety of industry partners. An efficient solution can only come about if companies either define a solution bilaterally with the most important partners, which is usually very time-consuming, or follow an established standard that considers cross-industrial application, such as EEBUS. In this cross-industry network manufacturers can very easily enter the solution business.
„Since our founding in 2012, EEBUS members have come from a variety of industries: I am convinced that this cross-industry approach is the main reason for our success as the communication interface standard for the low-voltage grid – it is impossible to imagine sector coupling in the context of energy transition if the interests of all sectors involved are not well aligned! “
Industrial Research Projects
One of EEBUS’ main activities is its active contribution to research and development: the initiative participates in various national as well as international funded projects devoted to developing the energy landscape of the future. Requirements and results deriving from these projects are important sources of input for the development of the EEBUS standard and vice versa.
Unit-e
How electromobility can be optimally integrated into the power grid is being investigated by the research project "unIT-e² - Reallabor für verNETZte E-Mobilität" in four field tests across Germany. To approach the complex topic from all sides at the same time, 29 partners from the automotive and energy industries, IT and charging infrastructure as well as science are participating in the joint project. The focus is on the user-friendly, large-scale implementation of bidirectional charging concepts. The three-year project is funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs And Climate Action (BMWK). Holistic solutions are being developed in the project for the further ramp-up of electromobility.
Main Achievement:
Grid Integration of electromobility
Test locations/sites:
Urban areas of Munich and Düsseldorf as well as rural based field tests in Eastern Bavaria, Lower Saxony, and Northern Hesse.
Working groups:
E-Mobility, HVAC, Inverter, Grid
Our Partners:
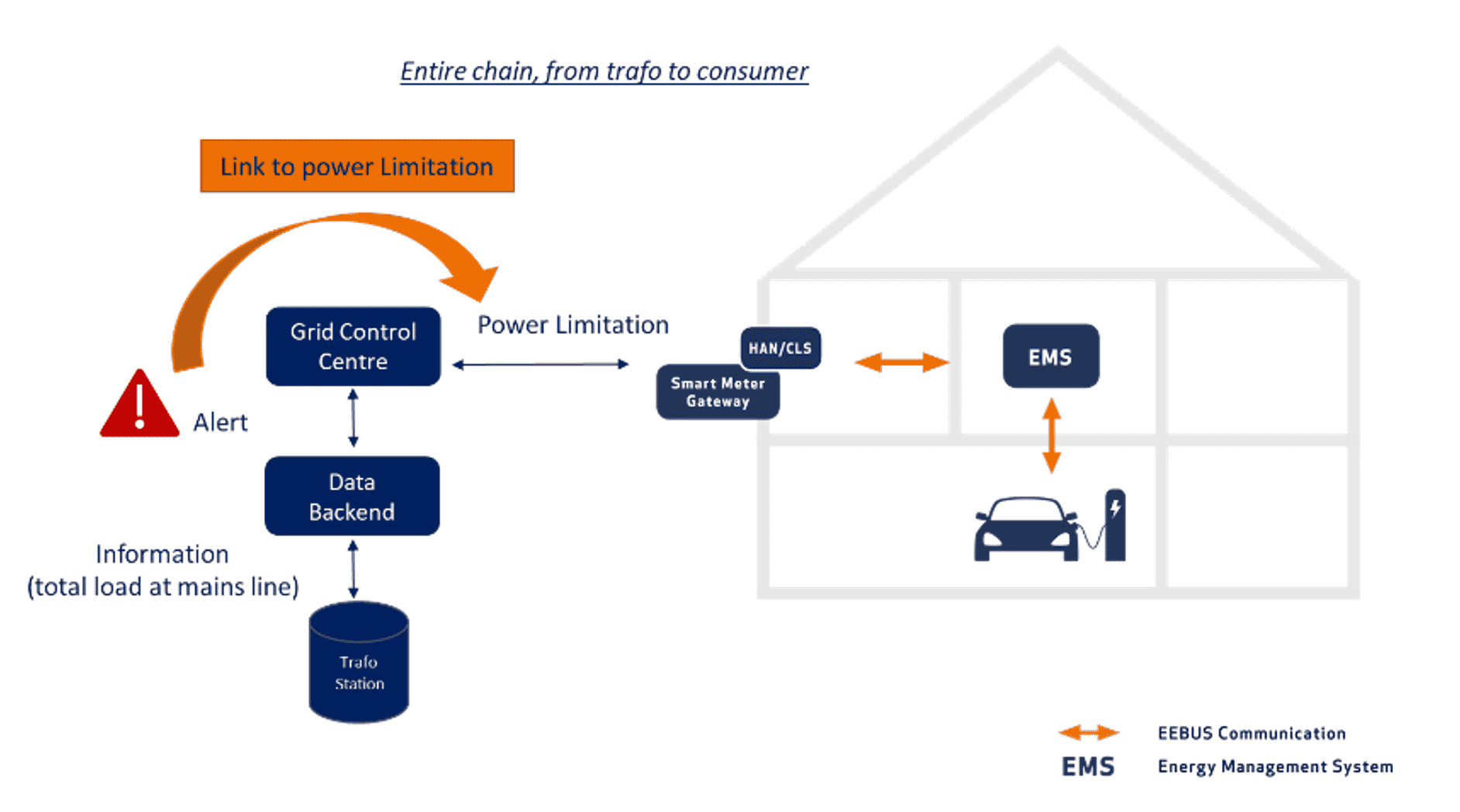
Fit4echange
The project focus lies on the increase of grid stability with a simultaneous ramp-up of e-mobility. Within Fit4echange, sensor and visualisation tools, allowing for increasing transparency in the current and prospected grid status, are to be developed as well as processes to inform the grid operator about an imminence grid congestion in advance. This information is necessary for the grid operator to react upon, i.e. by setting power limitations at the respective grid connection points via EEBUS communication.
Main Achievement:
Digitalisation and controllability of the low-voltage grid
Test locations/sites:
Duisburg region
Working groups:
E-Mobility, Grid
Our Partners:
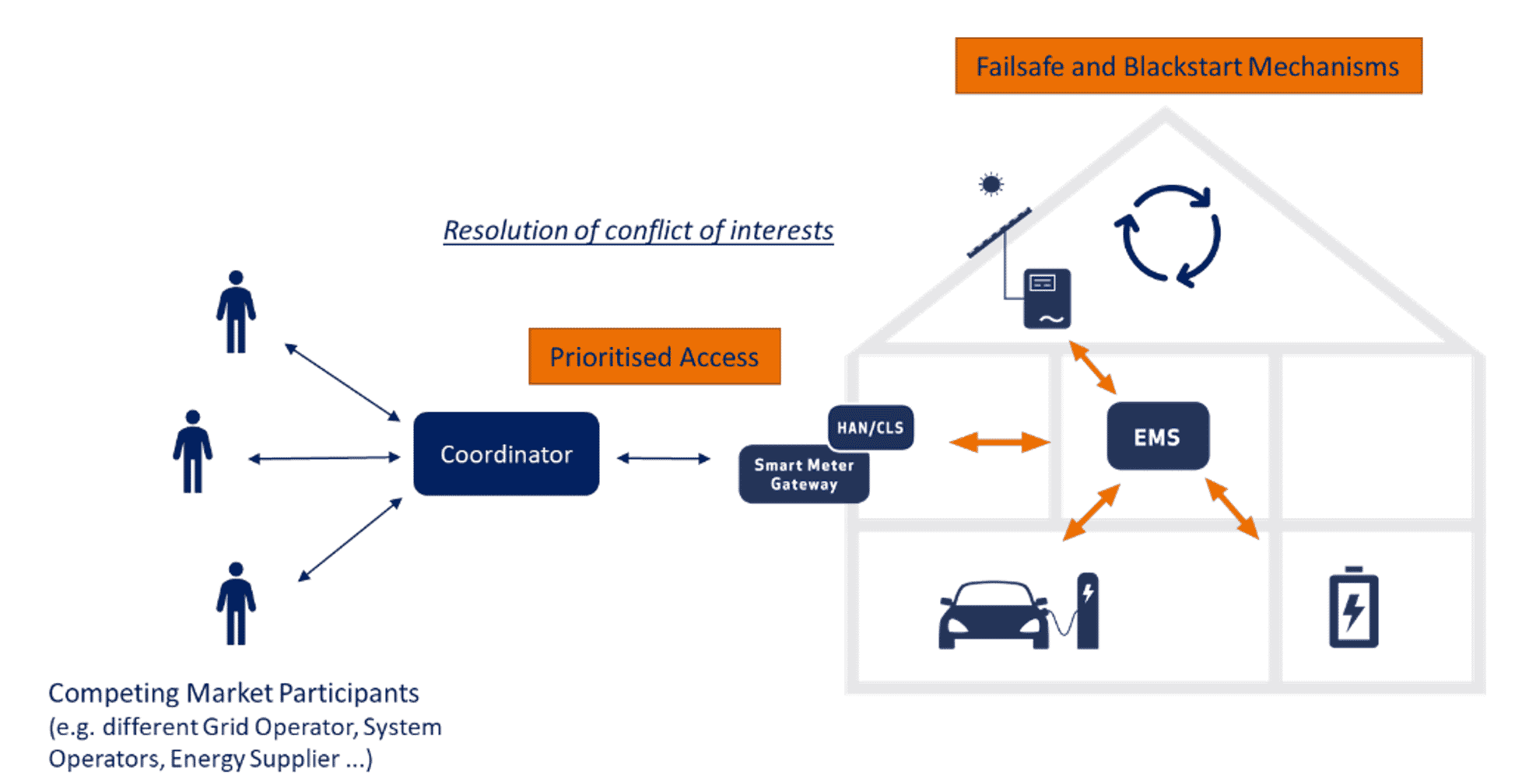
RESIGENT
In the near future, several market participants with correlating interests and control demands will reach the smart building and it’s devices. A grid operator could send a power limitation to reduce the total power consumption, while an aggregator sends a price incentive to increase the power consumption. In RESIGENT a coordinating entity that prioritise the signals from all market participants before reaching the building is to be developed. Furthermore failsafe and blackstart mechanisms are to be tested to power up devices and systems after a power or communication blackout.
Main Achievement:
Coordination of grid interaction
Test location/site:
Hassfurt region
Working Groups:
E-Mobility, Inverter, Grid,
Our Partners:
ARNi –Living Lab Cologne
Living Lab enables practical testing of interaction between end devices and the power grid, focusing on the interface of the building’s grid connection.
The test system considers the entire process chain: interoperable communication from the grid control centre to the end device is set up, documented, and tested. Connectivity of all devices < 100kW (e.g. Redispatch 2.0; §14a...) is to be developed according to German law and regulations. In addition, the location offers possibilities for sales and service training.
Main Achievement:
Practical test site for most current research topics related to smart grid connection
Location:
Cologne
Working Groups:
E-Mobility, HVAC, Inverter, Grid, Commercial
Our Partners:

Interconnect (EU)
EEBUS is leading the use case definition to enable an interoperable bi-directional communication from grid to device level to enable new services to all involved stakeholders. New services e.g. load management on building level – consumption and production – or time of use tariffs for cost optimized operation of devices will be tested in several pilots in 7 diffrent EU countries. The german pilot will show real full chain interoperability including Smart Meter Gateways in residential and commercial places to enable the transition in energy supply, mobility and heating.
Main Achievement:
Interoperability of European energy systems
Locations:
The project places the foundation for the future of smart energy management solutions by seven connected large-scale test-sites in Portugal, Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, Italy, Greece and France.
Project:
Ongoing
Our Partners:
C/- sells (Germany)
Various pilot installation to reduce buildings’ power consumption via Smart Meter Gateway (HAN/CLS interface) by power limitation set point from the DSO. EEBUS’s capacity management solution enables a control box or an energy manager to receive power limitation set points to power curtail electric vehicles or HVAC systems according to the customer preferences. Combined with monitoring of power consumption on building or device level hotsspots can be identified to avoid bottlenecks, so that cost-intensive grid expansion is not required in many cases.
Main Achievement:
Digitalisation of grid connection
Project:
Completed
Our Partners:
REnnovates (EU)
The largest European EEBUS implementation with over 240 residential buildings in the Netherlands. The EU lighthouse project “REnnovates” is a model for efficient plus-energy renovation throughout Europe. EEBUS enables manufacturer-independent energy management, paving the way for interaction with the Smart Grid.
REnnovates is only the beginning of the systematic and efficient renovation of existing building stock; it also holds great potential for new buildings throughout Europe. Further projects based on networked energy management and EEBUS are planned in the Benelux countries, Germany and Spain.
Main Achievement:
Energetic renovation of buildings
Project:
Completed